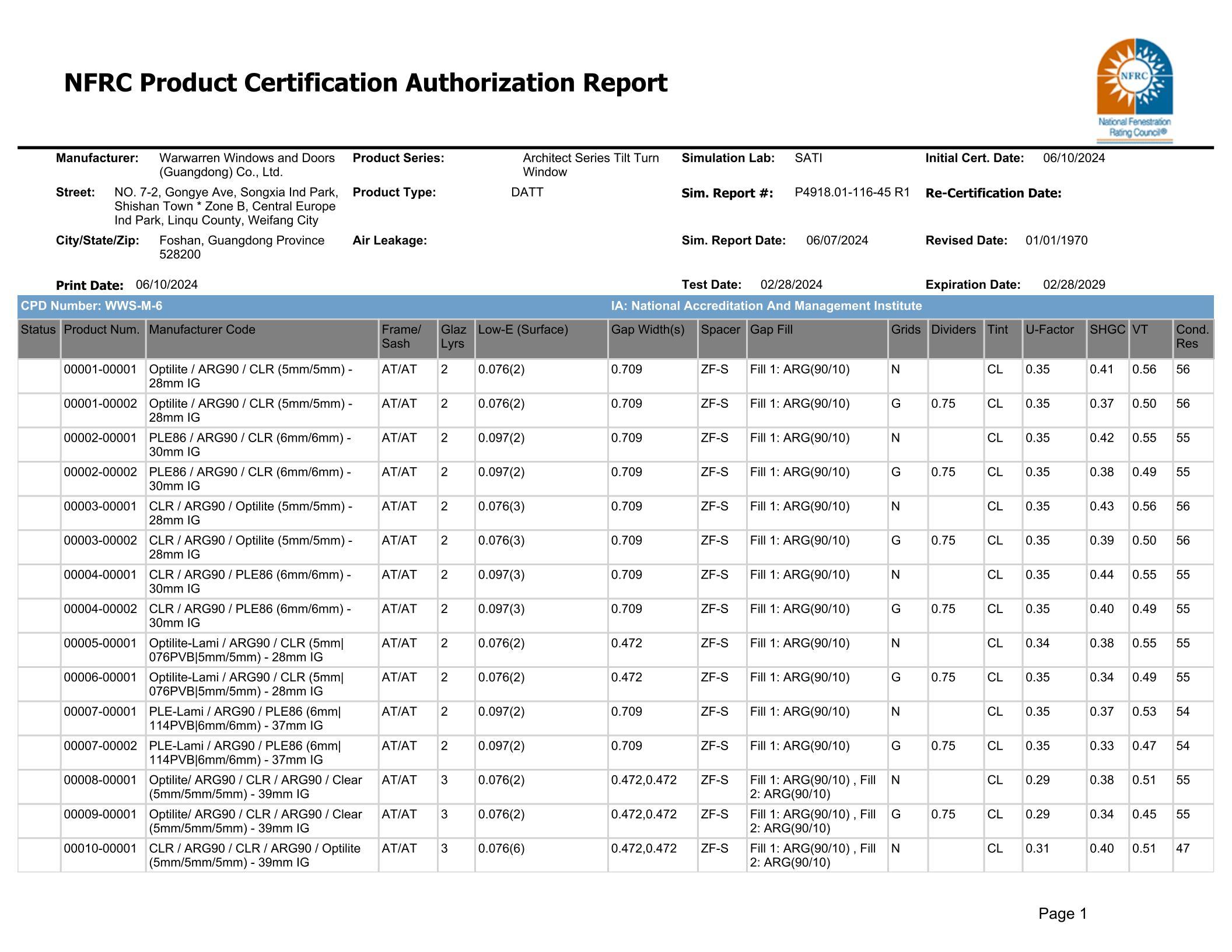
The advantages of Low-E glass windows
Release date:
2025-09-01
Low-E is short for "Low-Emissivity," referring to low-emission coated glass—a type of energy-efficient glass, as opposed to heat-reflective glass. Glass is a crucial building material, and with the ever-increasing demand for aesthetically pleasing architectural designs, its usage in the construction industry continues to grow. Yet today, when selecting glass doors and windows for buildings, people not only consider their visual appeal and appearance but also prioritize factors like thermal control, cooling costs, and achieving a comfortable balance between indoor sunlight exposure. This has made Low-E glass—the rising star within the coated glass family—stand out as a key focus of attention.
Excellent thermal performance
Heat loss through exterior window and door glass accounts for the largest portion of a building's energy consumption, making up more than 50% of the total. Research indicates that heat transfer from the inner surface of glass occurs primarily via radiation, contributing as much as 58% of the total thermal losses. This highlights that the most effective way to reduce heat energy loss is by improving the glass’s ability to minimize radiation from its inner surface.
Ordinary float glass has a high emissivity rate of up to 0.84; however, when coated with a low-emissivity (Low-E) film based on silver, its emissivity can be reduced to below 0.15. By using Low-E glass in building windows and doors, we can significantly curb the transfer of indoor heat to the outdoors via radiation, leading to impressive energy-saving benefits.
Another significant advantage of reducing indoor heat loss is its positive impact on environmental sustainability. During colder seasons, heating systems in buildings are major contributors to emissions of harmful gases like CO2 and SO2—key pollutants that harm both air quality and the environment. By installing Low-E glass, we can drastically cut down on fuel consumption required for heating, thereby reducing the overall emission of these pollutants.
It’s important to note that heat transfer through glass occurs in both directions—heat can move from indoors to outdoors, and vice versa—though the rate of transfer depends on the temperature difference between the two spaces. In winter, when indoor temperatures are higher than outdoor ones, maintaining warmth becomes critical. Conversely, during summer, when indoor temperatures are cooler than outdoor levels, it’s essential to prevent excessive heat from entering the building.
Low-E glass perfectly addresses these seasonal needs by providing superior insulation in winter and effective heat-blocking properties in summer. As a result, it not only enhances energy efficiency but also supports eco-friendly, low-carbon practices, helping to create healthier, more sustainable living environments.
Good optical performance: The visible light transmittance of Low-E glass ranges from a theoretical 0% to 95% (though achieving 95% with 6mm clear glass is extremely challenging), directly influencing the amount of natural light entering indoor spaces. Meanwhile, the outdoor reflectance typically falls between 10% and 30%, representing how much visible light is reflected back into the environment—essentially gauging the intensity of glare or brightness. Currently, China mandates that the visible light reflectance of curtain walls must not exceed 30%.
These unique properties of Low-E glass have led to its increasingly widespread adoption in developed countries. In contrast, China faces relatively limited energy resources, with per capita energy consumption significantly lower than global averages. Notably, building energy consumption already accounts for approximately 27.5% of the nation’s total energy use. Therefore, vigorously advancing the production technology of Low-E glass and expanding its application areas will undoubtedly yield substantial social and economic benefits.
During the manufacturing process, Low-E glass requires special attention due to its material properties. For instance, when passing through cleaning machines, it places stringent demands on the cleaning brushes used. The brush bristles must be made from high-quality nylon materials such as PA1010 or PA612, with an ideal diameter ranging from 0.1 to 0.15 mm. These bristles are prized for their exceptional softness, strong elasticity, and resistance to acids, alkalis, and high temperatures, enabling them to effortlessly remove dust from the glass surface without causing any scratches or damage.
Latest News
Contact Information
Contact Address: No. 7, Industrial Avenue East, Songxia Industrial Park, Shishan Town, Nanhai District, Foshan City
Warren Doors and Windows, south of Fangshan Road and west of Dongtai Road, Dongcheng Subdistrict, Linqu County, Weifang City, Shandong Province
Become A Deaters :Info@wolunmc.com
National customer service hotline:+86 400-676-9888
WhatsApp:+86-18866798677
Beijing customer service phone number:+86 010-68319888


Douyin

Xiaohongshu
E-mail:
Tel:
400:
The Little Red Book:
Tiktok:
WeChat:
在线客服添加返回顶部
页面顺滑的滚动
右侧在线客服样式 1,2,3 4
图片alt标题设置: Beijing Warren Doors and Windows Co., Ltd.
循环体没有内容时: Materials are currently being organized—stay tuned!
CSS / JS 文件放置地