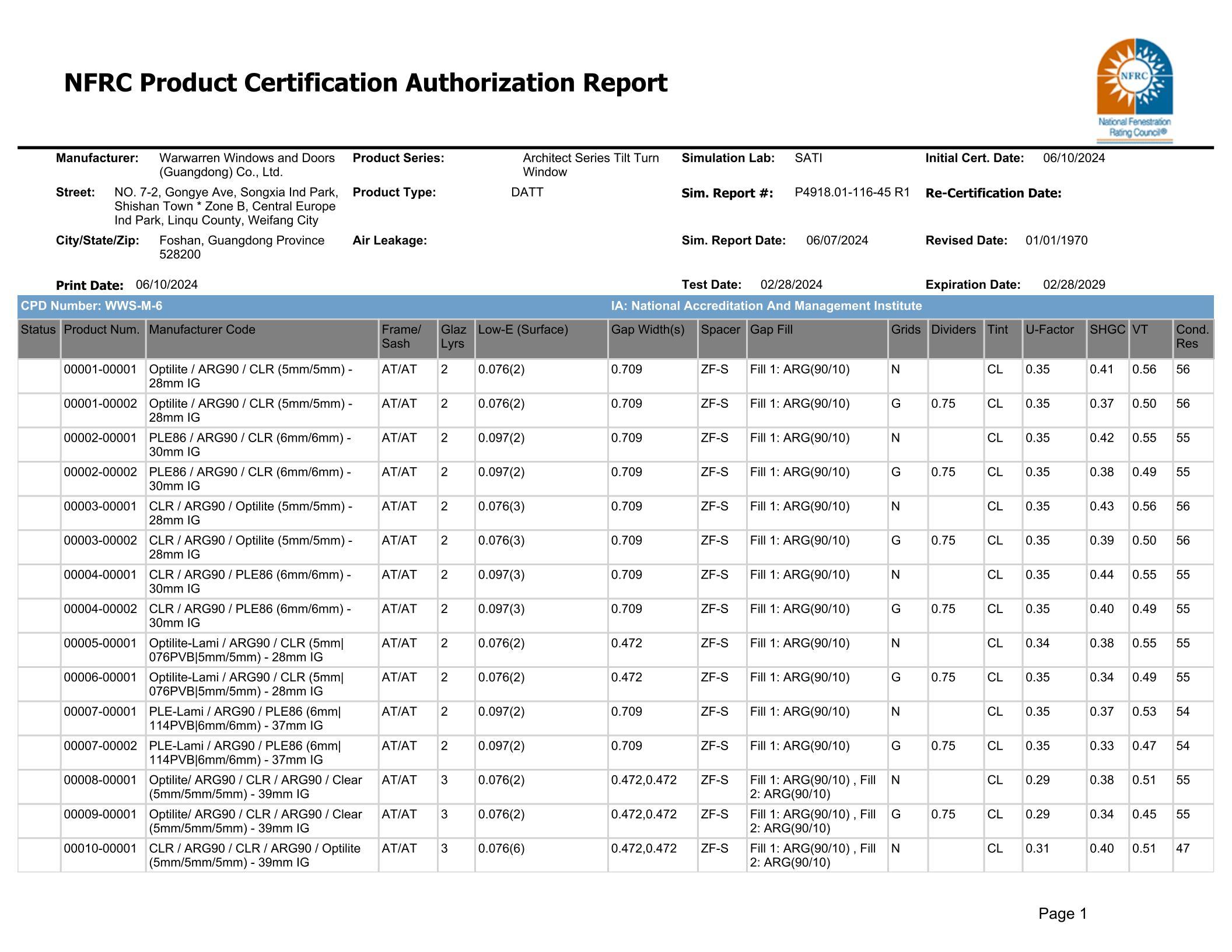
Does your home's insulated glass contain an inert gas?
Release date:
2025-09-01
As the nation’s energy-saving policies are increasingly and effectively implemented, building energy efficiency requirements are also steadily rising. Consequently, architectural glass products are evolving toward high-performance insulated glass units. In addition to the low-emissivity coated insulated glass units that are already gaining widespread adoption, there is a growing trend of using insulating glass with inert gases—such as argon or helium—filled in the space between the panes. Compared to air, these inert gases have higher density and lower thermal conductivity, which helps slow down heat convection within the interlayer and reduces the overall thermal transfer through the gas-filled cavity. As a result, the U-factor of the insulated glass unit is lowered, significantly enhancing its thermal insulation performance and boosting energy efficiency.

Types of noble gases Noble gases
Noble gases include helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). All noble gases are colorless, odorless, non-toxic, single-atom molecules in the gaseous state. They belong to Group 18 of the periodic table, where their outer electron shells are already fully saturated, making them extremely unreactive.
Among the inert gases used as fillers in insulated glass units, argon, krypton, and xenon are commonly employed. Of these three gases, argon is the most abundant in air—making up about 1% of the atmosphere—and it’s relatively easy to extract, making it more affordable. As a result, argon is the most widely used inert gas for filling the air space within insulated glass units.
The Role of Inert Gas Filling in Hollow Glass
Hollow glass is filled with inert gas, enhancing its insulation properties and making it more energy-efficient compared to standard hollow glass that lacks this feature. In winter, it helps retain heat indoors, while in summer, it effectively blocks heat from entering the room.

Inflating it reduces the pressure difference between the inside and outside, maintaining pressure balance and minimizing glass breakage caused by pressure disparities.
After being filled with argon gas, the K-value of insulated glass units can be effectively improved, reducing condensation on the indoor-side glass and enhancing overall comfort—meaning that argon-filled insulated glass is less likely to experience dew formation or frost buildup.
Thanks to argon gas's inherent properties as an inert gas, it can slow down heat convection within insulated glass units while also significantly enhancing their soundproofing and noise-reduction performance—effectively improving both the thermal insulation and acoustic benefits of the glass.
Because the gas being filled is a dry, inert gas, it displaces the moisture-laden air inside the hollow glass cavity, keeping the internal environment dry and extending the lifespan of the molecular sieve within the aluminum spacer frame.
Standards for filling insulated glass with inert gas.
There are no specific industry regulations regarding how much inert gas should be filled inside insulated glass units, but generally, the amount should not fall below 90%.
Latest News
Contact Information
Contact Address: No. 7, Industrial Avenue East, Songxia Industrial Park, Shishan Town, Nanhai District, Foshan City
Warren Doors and Windows, south of Fangshan Road and west of Dongtai Road, Dongcheng Subdistrict, Linqu County, Weifang City, Shandong Province
Become A Deaters :Info@wolunmc.com
National customer service hotline:+86 400-676-9888
WhatsApp:+86-18866798677
Beijing customer service phone number:+86 010-68319888


Douyin

Xiaohongshu
E-mail:
Tel:
400:
The Little Red Book:
Tiktok:
WeChat:
在线客服添加返回顶部
页面顺滑的滚动
右侧在线客服样式 1,2,3 4
图片alt标题设置: Beijing Warren Doors and Windows Co., Ltd.
循环体没有内容时: Materials are currently being organized—stay tuned!
CSS / JS 文件放置地