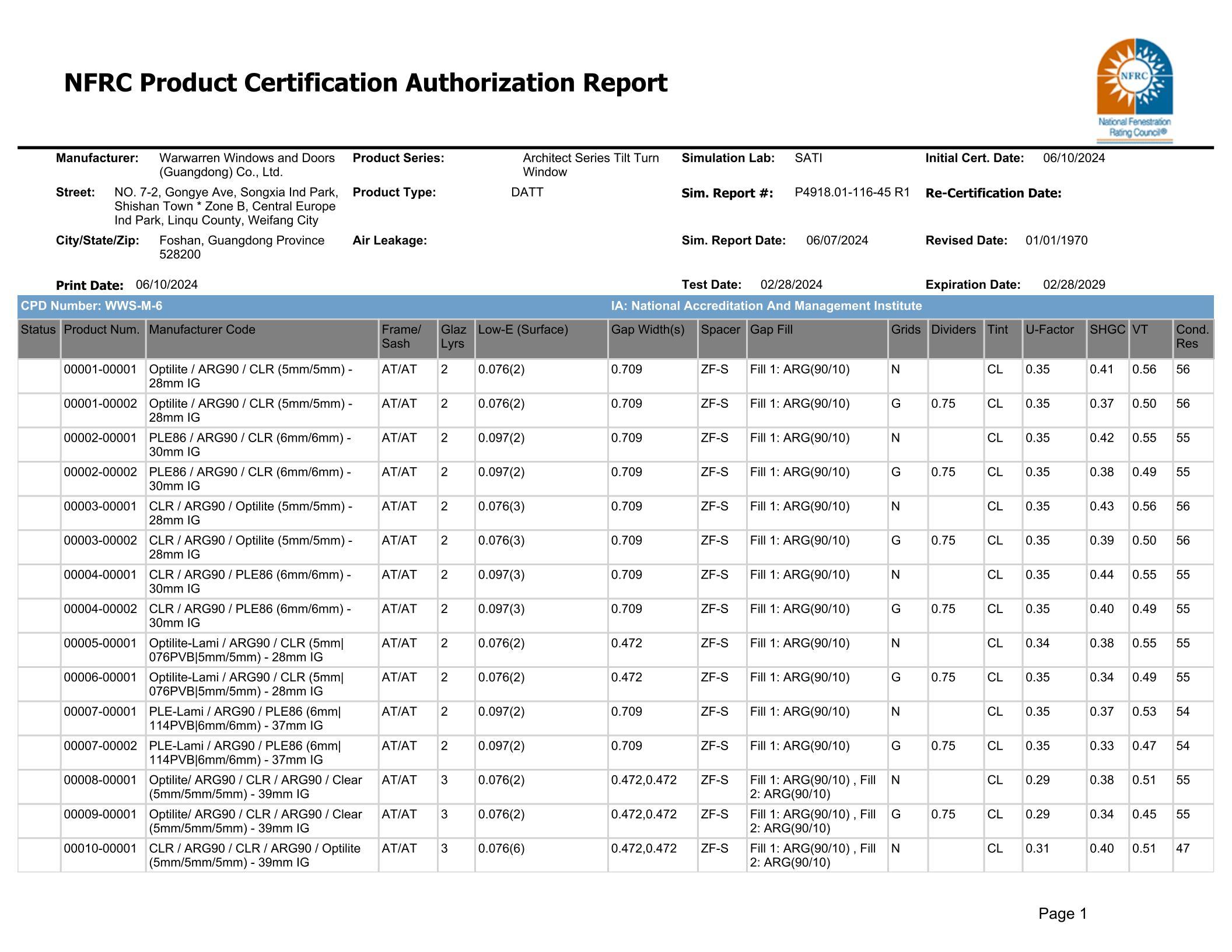
Comparison between断桥铝 doors and windows and PVC doors and windows:
The single, monotonous white color of plastic doors and windows is a significant drawback, failing to meet the diverse aesthetic demands of modern architectural facade designs. In contrast, thermal break aluminum doors and windows offer a wide range of surface treatment options—such as powder coating, anodizing, electrophoretic coating, and wood-grain transfer printing—enabling an extensive palette of colors, including white, green, and even intricate wood or granite-inspired finishes.
Through the objective comparison above, while broken bridge aluminum doors and windows fall short in terms of thermal insulation compared to other materials, they outperform plastic steel doors and windows in every other aspect. This is precisely why broken bridge aluminum doors and windows have become so popular today—and why they enjoy such a high market share.
Second, a comparison of air-tightness performance
Plastic-steel doors and windows, since their frame and sash components are welded together, should have slightly better air tightness compared to aluminum alloy doors and windows connected with screws. However, broken-bridge aluminum door and window profiles offer higher dimensional accuracy, resulting in a tighter fit between the frame and sash.
Third, a comparison of thermal insulation performance
Aluminum-clad break-bond windows and doors don’t offer as good thermal performance as PVC-U windows and doors. Additionally, the aluminum alloy frame and sash account for about 10% less of the total window area compared to their PVC-U counterparts. Moreover, the aluminum frames and sashes aren’t solid—instead, they feature hollow profiles—and the wall thickness of these hollow aluminum profiles (which effectively acts as a thermal bridge) is roughly 40% thinner than that of plastic profiles.
Fourth, a comparison of daylighting performance
Plastic-steel doors and windows have poorer daylighting performance compared to aluminum alloy ones, with their frame and sash components blocking about 10% more light. This results in reduced visibility and less attractive decorative effects, ultimately making it less conducive to energy-efficient building lighting and lower energy consumption.
Fifth, comparison of soundproofing performance
The soundproofing performance of a window primarily depends on the sound-insulating effectiveness of the glass, which accounts for about 80% of the window area. Both broken-bridge aluminum doors and windows, and PVC steel doors and windows, feature roughly the same level of gap sealing—and consequently, their soundproofing performance is also comparable.
Sixth, a comparison of fire resistance performance
Flame-retardant PVC plastic doors and windows have better fire resistance compared to combustible wood doors and windows, but they still lag behind non-combustible, thermally broken aluminum alloy doors and windows. When it comes to the fire performance of doors and windows, steel and aluminum models fare relatively well, while plastic and wood options tend to perform less effectively.
Seventh, a comparison of lightning protection and electrostatic issues
Aluminum-clad PVC doors and windows are good conductors of electricity, making them suitable for use as lightning protection systems and effective in preventing static electricity buildup. According to available information, to address static electricity issues in plastic materials, especially in fire safety contexts, an antistatic coating containing quaternary ammonium salts can be applied to the surface, helping it absorb moisture from the air and significantly boosting conductivity. However, currently, none of the domestically produced plastic doors and windows have undergone treatment with such antistatic coatings.
Eighth, a comparison of decorative issues
The single, monotonous white color of plastic doors and windows is a significant drawback, failing to meet the diverse aesthetic demands of modern architectural facade designs. In contrast,断桥铝 (thermal break aluminum) doors and windows offer a wide range of surface treatment options—such as powder coating, anodizing, electrophoretic coating, and wood-grain transfer printing—allowing for an extensive palette of colors, including white, green, and even intricate wood or granite-inspired finishes.
Through the objective comparison above, while断桥铝门窗 (broken bridge aluminum doors and windows) fall short in terms of thermal insulation compared to other materials, they outperform plastic steel doors and windows in every other aspect. This is precisely why broken bridge aluminum doors and windows have become so popular today—and why they enjoy such a high market share. |
|